The artificial intelligence landscape is shifting from passive chatbots to autonomous agents that can plan, reason, and execute complex workflows. However, for this “agentic era” to reach its full potential in the enterprise, these systems must move beyond isolated prototypes and into a unified, interoperable ecosystem. To accelerate this transition, industry titans OpenAI and Cisco have announced a strategic commitment to backing open standards aimed at scaling agentic AI.
The Push for Interoperability in Agentic AI
As businesses deploy an increasing number of AI agents—ranging from customer support bots to automated coding assistants—a critical challenge has emerged: fragmentation. Currently, most AI agents operate within “walled gardens,” unable to communicate with agents from different vendors or securely access diverse data sources without custom, brittle integrations.
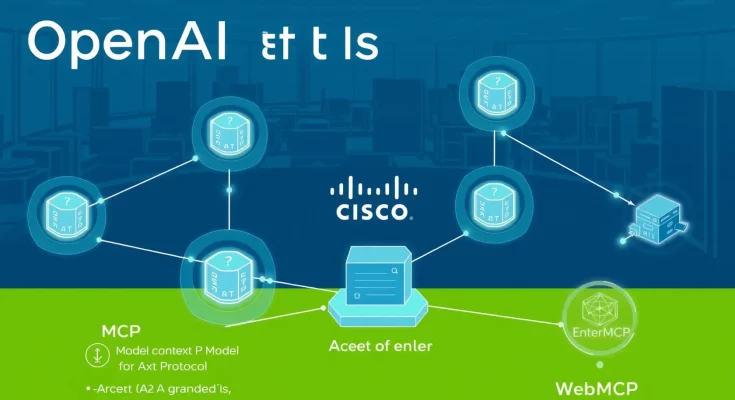
To solve this, OpenAI and Cisco are championing the development of universal protocols. By joining forces through initiatives like the Agentic AI Foundation (AAIF), hosted by the Linux Foundation, these companies aim to establish the “TCP/IP of AI.” Just as standardized internet protocols allowed the web to scale, these new AI standards will enable agents to discover, authenticate, and collaborate with one another seamlessly across different platforms.
Key Standards Driving the Change
The collaboration centers on several emerging protocols designed to handle the unique requirements of autonomous systems. These standards focus on three primary areas: context sharing, secure communication, and transactional capabilities.
- Model Context Protocol (MCP): Originally introduced by Anthropic and now a core project of the AAIF, MCP provides a universal standard for connecting AI models to tools and data repositories. By backing MCP, OpenAI and Cisco ensure that agents can maintain consistent context as they move between different enterprise applications.
- Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol: This standard focuses on how agents negotiate and delegate tasks. It allows a high-level “orchestrator” agent to break down a project and assign sub-tasks to specialized agents, even if those agents are built on different underlying models.
- WebMCP: A browser-based extension of the context protocol, WebMCP allows websites to expose structured “tools” to AI agents, replacing the need for unreliable web scraping with direct, function-based interactions.
This push for standardization is closely linked to the launch of OpenAI Frontier, which serves as a centralized management hub for these emerging agentic workforces.
Cisco Infrastructure Meets OpenAI Intelligence
The partnership leverages the unique strengths of both companies. Cisco, the global leader in networking and security, provides the underlying infrastructure required to handle the massive data flows of agentic systems. For AI agents to scale, the network must be “AI-ready,” offering low latency and robust security at the edge.
OpenAI contributes the advanced reasoning capabilities of its latest models. By aligning their technical roadmaps, the two companies are working to ensure that enterprise networks can automatically recognize and prioritize AI agent traffic. This includes developing “Agentic Networking” capabilities, where the network itself acts as a platform for hosting and securing agent interactions.
Solving the Trust Gap
Perhaps the most significant hurdle to agentic AI adoption is trust. Businesses are often hesitant to give autonomous agents access to sensitive data or financial authority. The new standards prioritize governance and transparency. Through standardized logging and “proof of intent” protocols, organizations can maintain a clear audit trail of every action an agent takes, ensuring compliance with internal policies and external regulations.
The Massive Economic Potential of Agentic Systems
The move toward standardization comes as the market for agentic AI is poised for exponential growth. Industry analysts expect the global agentic AI market to surge from approximately $5.2 billion in 2024 to nearly $197 billion by 2034. This growth is driven by the promise of dramatic productivity gains as agents take over repetitive digital tasks.
In the enterprise, this transformation is already visible in how AI agents redefine SaaS workflows. Instead of users navigating multiple dashboards, agents will interact with software via standardized APIs, executing end-to-end processes like procurement, financial reporting, and complex data analysis with minimal human oversight.
What This Means for the Future of Business
For IT leaders and decision-makers, the backing of standards by OpenAI and Cisco sends a clear message: The era of isolated chatbots is over. To prepare for the next decade of innovation, businesses should focus on three strategic pillars:
1. Prioritizing Interoperable Frameworks
Avoid vendor lock-in by selecting AI tools and platforms that commit to open standards like MCP. This ensures that the agents you build today will be able to integrate with the tools you adopt tomorrow.
2. Investing in AI-Ready Networking
As agents become more active within the corporate environment, the demands on internal networks will shift. Modernizing infrastructure to support high-speed, secure AI traffic is no longer optional; it is a prerequisite for scaling autonomous operations.
3. Developing “Human-in-the-Loop” Governance
Standards provide the technical foundation for trust, but businesses must still define the ethical and operational guardrails for their agents. Establishing clear hierarchies of authority and review processes will be essential as agents move from recommendation to execution.
The collaboration between OpenAI and Cisco marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of artificial intelligence. By building a shared language for autonomous systems, they are laying the groundwork for a world where AI doesn’t just answer questions, but actively powers the machinery of global commerce.